REALWORLDFARE
Realworldfare is an inclusive private community rooted in equity, education, and conscious empowerment. We are committed to demystifying the legal and commercial frameworks that silently govern everyday life—bringing clarity to the often-hidden distinctions between rights, privileges, and obligations. Through fair and uncensored information, we support truth-seekers in reclaiming their private power.
Our platform offers educational resources and networking opportunities focused on Common Law, Constitutional Law, Equity, Public and Private Law, Trust and Contract Law, UCC Filings, Private Banking, Debt Instruments, Foreclosure Defense, Estate Planning, and lawful dealings involving Negotiable Instruments, Deeds, Bonds, and Commercial Equity.
We uphold that equity corrects what law cannot, and that the restoration of private remedy begins with comprehension. In a world increasingly dominated by the color of law, coercion, and administrative overreach, Realworldfare serves as a sovereign resource for those who choose to operate in truth, honor, and informed peace
Commonly misinterpreted and/or terms: individual, bank, financial institution, person, state Citizen, national, U.S. citizen, secured party, trust, attorney in fact, attorney at law, lawyer, minor, infant, discharge, pay, payment.
SEARCH WEBSITE
LATEST NEWS
Federal Courts Unequivocally Acting as a Criminal Enterprise: How the Central District of California Systematically Violates Rule 8, Rule 55, Rule 56, and Due Process in a Full Constitutional Collapse
The Central District of California is no longer functioning as a lawful Article III tribunal. It is operating as a coordinated mechanism of obstruction—systematically ignoring Rule 8, refusing mandatory Rule 55 defaults, and suppressing Rule 56 evidence in open defiance of due process. This pattern is not accidental but structural, presenting all hallmarks of a federal judiciary acting as a criminal enterprise under color of law. The result is a full constitutional collapse in which rights cannot be enforced, remedies cannot be obtained, and justice has been replaced with procedural illusion. Immediate Supreme Court intervention is not optional—it is constitutionally required.
Read MoreHow Non-Judicial Foreclosures are Unconstitutional and Illegal Takings: Homeowners Lose Property After Banks Are Already Paid in Full
Non-judicial foreclosure is an unconstitutional taking that violates due process and property rights by letting private actors seize homes without proving a debt is owed. Banks are often paid twice — or more — through insurance and investor payouts before they foreclose, yet still commit property theft with no courtroom oversight. At the same time, the note and deed are frequently split, destroying any lawful right to enforce foreclosure but ignored in practice. This article exposes how millions lose their homes through a non-judicial system engineered to bypass Constitutional protections and strip homeowners of their rights.
Read MoreTHE PRIVATE LITIGATORS GROUP™: KNOWLEDGE, POWER, EQUITY, & ENFORCEMENT
The Private Litigators Group™ is a private, invitation-only alliance for living men and women who refuse to be silenced or railroaded by corrupt courts, predatory BAR attorneys, and color-of-law abuses. We empower members with bulletproof sui juris strategies, verified complaints, federal jurisdiction mastery, and the administrative tools needed to stand above the system—not beneath it. This is not public lawyering; it is private knowledge, private contract, and private power. Reclaim your standing, enforce your rights, and end the courts’ reliance on your ignorance. Membership is limited and strictly private.
Read MoreIMMUNITY STRIPPED: Verified Complaint for RICO, Bivens Violations, and Constitutional Torts Against Federal and State Judges Sunshine Sykes and Raquel Marquez, and Attorneys John and Therese Bailey for colluding, engaging in fraud, and acting ultra vires and WITHOUT jurisdiction
A groundbreaking verified complaint has been filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia naming Federal Judge Sunshine Suzanne Sykes, State Judge Raquel A. Marquez, and attorneys John and Therese Bailey in a RICO and Bivens action for fraud, collusion, and ultra vires acts. The suit exposes coordinated judicial misconduct, void orders, and abuse of power carried out without jurisdiction or immunity. This case marks a historic challenge to the illusion of judicial untouchability and a direct demand for accountability before a jury of the People.
Read MoreTHE PEOPLE ARE SOVEREIGN Affirmed by the State Constitutions and the Constitution for the United States of America
This declaration proves what every Constitution in America already affirms — the People are sovereign. Drawn directly from all fifty State Constitutions and the Constitution for the United States of America, this document exposes how all lawful power originates from the People and is only delegated to government by consent. It stands as irrefutable, judicially noticeable evidence that judges, attorneys, clerks, sheriffs, and politicians are mere trustees and servants of the People’s authority. A must-read for anyone ready to understand where real sovereignty and lawful power truly reside.
Read MoreALL LOANS, MORTGAGES, AND PUBLIC UTILITY BILLING CONTRACTS OPERATE AS GOVERNMENT OBLIGATIONS
This article exposes how every loan, mortgage, and public utility billing contract operates as a federally recognized government obligation — not a private contract. Backed by statutes like 18 U.S.C. § 8, 12 U.S.C. § 411, and 31 U.S.C. § 3123, the credit you generate is monetized and guaranteed by the United States Treasury. Banks and utility companies merely act as intermediaries, while your signature creates the actual value. This legal breakdown reveals the true debtor-creditor dynamic hidden behind everyday commerce. The truth isn’t theory — it’s codified in law.
Read MoreTHE DTCC: WAREHOUSING THE WORLD’S ENERGY THROUGH SECURITIES FRAUD
This exposé uncovers how the Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (DTCC) secretly holds legal title to your birth bond, court judgments, and financial instruments — without consent, disclosure, or remedy. Through nominee shell CEDE & Co., and in coordination with the U.S. Treasury and Federal Reserve, your estate is monetized and cleared as a security. Backed by statutes, case law, and the Uniform Commercial Code, this article reveals how to collapse the presumption and reclaim your lawful status as the secured party creditor. This is not theory — this is codified commercial enslavement by silence and inaction. Read it. Reclaim it.
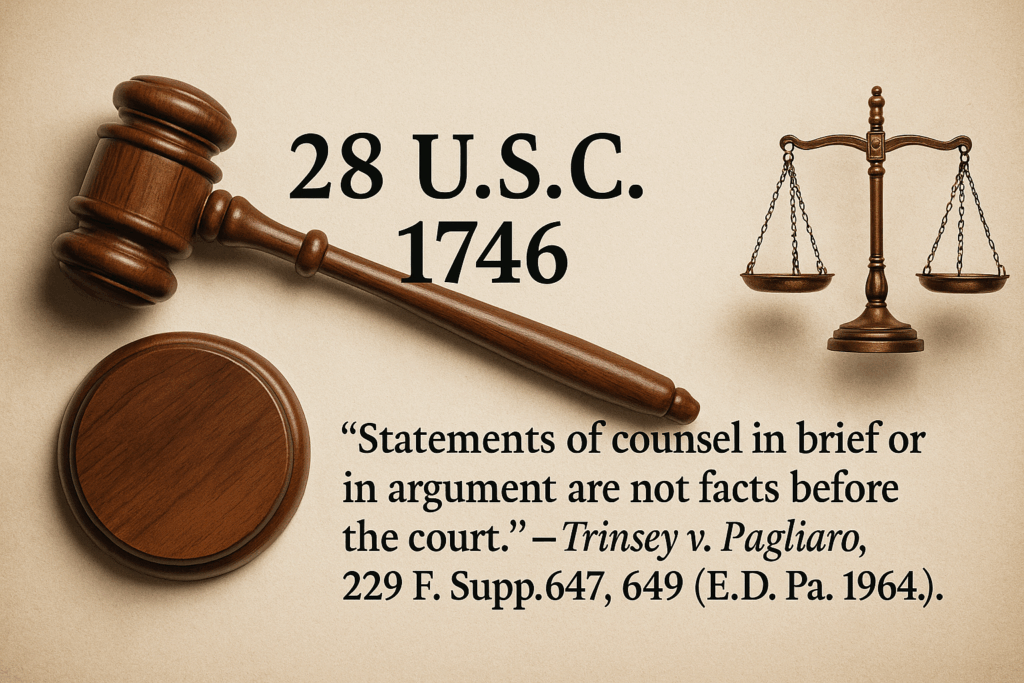
Read MoreVerified Truth and the Collapse of Jurisdiction: When Courts Ignore 28 U.S.C. § 1746
This article establishes that verified filings under 28 U.S.C. § 1746 constitute sworn evidence equal to notarized affidavits and, when unrebutted, stand as final truth in law. Supported by Rule 8(b)(6) and Rule 56, it demonstrates that verified facts must be admitted and summary judgment becomes mandatory once no genuine dispute remains. Federal precedent confirms that attorney argument is not evidence (Trinsey v. Pagliaro, 229 F. Supp. 647) and that verified complaints carry full evidentiary weight. Under the Clearfield Doctrine, all statutory and public acts are commercial, binding officials to the same evidentiary standards as private parties. Any judicial act ignoring verified truth is ultra vires, void ab initio, and actionable under 42 U.S.C. § 1983 and Bivens v. Six Unknown...
Read MoreThe Great Overlay: The BAR-Run Conversion of Americans into Wards — The Codification Process From Organic Sovereignty to Corporate Statutory Rule
What began as freedom under Natural Law has been hijacked by statutes, attorneys, and codification into a corporate empire. The Great Overlay dismantles the illusion of justice by showing how BAR-run courts reduce men and women to incompetent wards while enforcing color of law. This is a devastating breakdown of the fraud behind “U.S. citizenship” and the unlawful corporate overlay that replaced the republic.
Read MoreFEATURED SERVICES & PRODUCTS
-

The Great Conversion and The “Legal” Architecture of Enslavement: How America Was Converted from a Republic of Sovereign People into a Corporate-Financial Trust System and How Sovereignty Was Replaced with Statutory Slaver
$79.99 Add to cart -

The UCC Playbook: How to Use Contract Law to Secure Your Assets, Family, Freedom, and Enforce Your Rights
$999.99Original price was: $999.99.$33.33Current price is: $33.33. Add to cart -

Eliminate PURPORTED “Loan” on private Automobile, Recoup Assets, Payments, and ALL Money Paid
$6,000.00 Buy product -

Discharging Debt Through Equity Remedy: Vehicle, Mortgage, and Credit Relief
$10,000.00Original price was: $10,000.00.$6,000.00Current price is: $6,000.00. Add to cart -

The Declaration of Independence as Trust Law: Government as Trustee, The People as Beneficiaries
$0.00 Add to cart -

Mortgage Cancelation + Transfer Home/House/Property to Trust + Trust Creation and Litigation Protection
$6,600.00 Buy product -

™SOVEREIGN BLUEPRINT© An educational guide of Truth for reclaiming your assets, rights, and birth estate
$3,000.00Original price was: $3,000.00.$43.33Current price is: $43.33. Add to cart -

Private Consultations (Phone, Video, Private 1 on 1)
$333.00 SCHEDULE CONSULTATION -

Virtual Class: Introduction to Private Law, Contracts, and Estate Rights
$1,000.00Original price was: $1,000.00.$333.00Current price is: $333.00. ENROLL IN CLASS
INFORMATION BRIEFS
-

Why There Have Been No True Article III Judges Since 1989 — 1989 Judicial Improvements Act
$0.00 Add to cart -

Fraud by Design: How States, Counties, Cities, and Sheriffs Operate as Corporations Under Color of Law
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Administrative Procedure Act, the Fifth Amendment (Constitution), and the Power of Due Process of Law
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Great Overlay: The BAR-Run Conversion of Americans into Wards — The Codification Process From Organic Sovereignty to Corporate Statutory Rule
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Truth About Modern “Lending”: How You are the Creditor, Your Signature Funds the System and Enslaves You Through Fraud, Credit, and “Legal” Deception
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Supreme Hierarchy of Law: From Natural Rights to Codification
$0.00 Add to cart -

When Judges Act Without Jurisdiction = Void Orders, No Immunity, Full Personal Liability, Judicial Usurpation, Ultra Vires Acts, Judicial Treason, and Commercial Fraud
$0.00 Add to cart -

The 13th & 14th Amendments: How Slavery(Servitude) Was Made Voluntary(via Contracts) and the Corporate U.S. Citizen (Ens Legis) Was Created
$0.00 Add to cart -

state Citizen aka One of the People vs. “citizen of the United States” (sole proprietor/estate/ens legis): The 14th Amendment Divide Between the “United States” (federal corporation) and the “united states of America” (sovereign states)
$0.00 Add to cart
MEMORANDUMS OF LAW
-

$SUIJURIS Crypto Coin Mint
$0.25 Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF POINTS AND AUTHORITIES: FRAUD VITIATES EVERYTHING, AND THAT A FORECLOSURE OR TRUSTEE’S SALE BASED ON FRAUD IS VOID AB INITIO
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

Memorandum of Law: Right to Represent Your Trust or Estate 28 U.S.C. §§ 1654, 2072, Rule 17, the UCC, and the Constitution
$29.99 Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF LAW In Support of the Position That the Court Has Lost Jurisdiction and Its Orders Are Void Ab Initio
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF LAW IN SUPPORT OF 1099OID – ORIGINAL ISSUE DISCOUNT
$0.00 Add to cart -

GENERAL MEMORANDUM OF LAW Re: Misuse of the Term “Sovereign Citizen” as a Sanctionable, Prejudicial, and Defamatory Violation of Judicial Standards, Due Process, and Ethical Conduct
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF POINTS AND AUTHORITIES IN SUPPORT OF CORRECT DISTINCTION BETWEEN “SUI JURIS”, “IN PROPRIA PERSONA”, AND “PRO SE”
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF POINTS AND AUTHORITIES IN SUPPORT OF APPELLATE JURISDICTION UNDER 28 U.S.C. § 1447(d) FOLLOWING REMOVAL PURSUANT TO 28 U.S.C. § 1443(1)
$0.00 Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF LAW: IN SUPPORT OF REGISTERED MAIL AS VALID SERVICE OF PROCESS
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart
FEATUTRED VIDEOS
REVIEWS
Ev3ryone needs to know

Excellent work, this comes from a natural man [Sui Juris] that has studied for years and has the fundamental innerstanding, and over standing to interpret and know 100% that the processes, Affidavits and forms offered here are of the highest quality.
Who better to work with, than those that can directly relate to you?

Man o man is this a great read and a life changer. I can see why it would be a $3,000 purchase. The amount of curated information you get in this is well worth over $3,000. Years of information all spelled out for you.
Changed my life and I am forever grateful to the author and person that referred me to this. I am 20+ year accountant and I did not know a lot of what is contained in this book. All verifiable and it comes with ample amounts of referenced proof. The “matrix” is real and this book really breaks it all down fundamentally.
Smooth process and the end results were just as described. I cant thank the Realworldfare team enough! Still learning and beyond grateful for setting me free.

MANUALS, HANDBOOKS, STUDIES
-

How the Act of 1871, the Federal Reserve Act of 1913, the Trading With the Enemy Act of 1917, the 1933 Bankruptcy, and the IRS Puerto Rico Trust Captured America
$0.00 Add to cart -

THE SIGNIFICANCE OF STAMPS USED ON BANK NOTES By Arnold Keller and John Sandrock
$0.00 Add to cart -

1928 CITIZENSHIP TRAINING MANUAL
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Great Overlay: The BAR-Run Conversion of Americans into Wards — The Codification Process From Organic Sovereignty to Corporate Statutory Rule
$0.00 Add to cart -

SECRETS OF THE SOCIAL SECURITY NUMBER
$0.00 Add to cart -

LAW-Points and Authorities in Support of International Bill of Exchange
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Story of The Social Security Number by Carolyn Puckett
$0.00 Add to cart -

Why There Have Been No True Article III Judges Since 1989 — 1989 Judicial Improvements Act
$0.00 Add to cart -
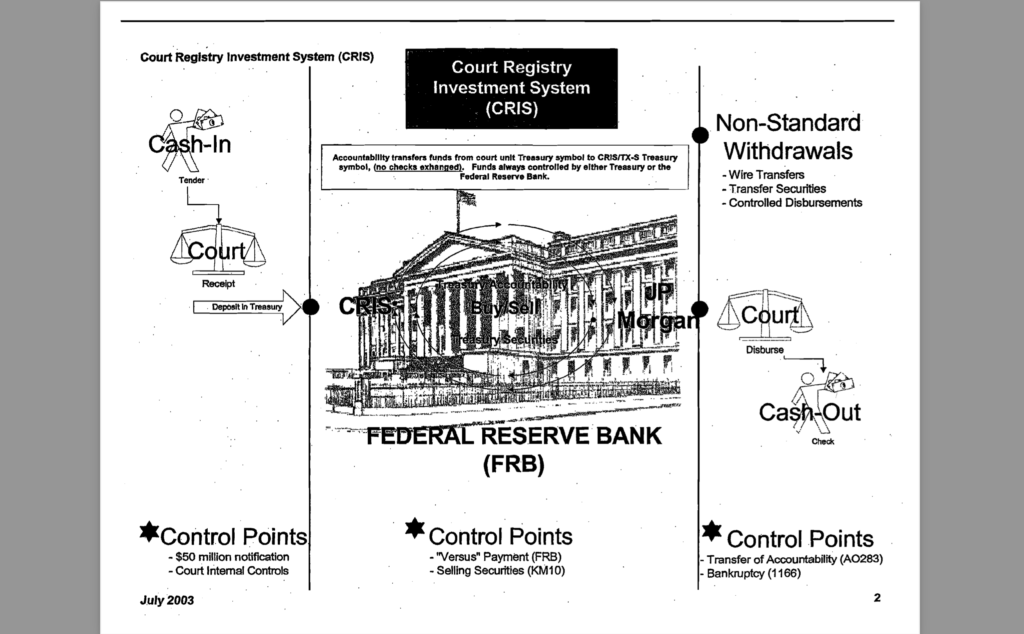
IT’S ALL COMMERCE: CRIS (Court Registry Investment System) Analysis and Breakdown
$0.00 Add to cart
TEMPLATES
-

NOTICE OF DEFAULT TEMPLTE – 2010-01
$150.00Original price was: $150.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

Affidavit of Revocation & Termination of Franchise
$150.00 Add to cart -

Notice of Default and Opportunity to Cure (Template 001)
$150.00Original price was: $150.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

AFFIDAVIT CERTIFICATE of NON-RESPONSE, DISHONOR, JUDGEMENT, and LIEN Authorization
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$99.00Current price is: $99.00. Add to cart -

MEMORANDUM OF POINTS AND AUTHORITIES IN SUPPORT OF VERIFIED MOTION FOR MANDATORY JUDICIAL RECUSAL UNDER 28 U.S.C. §§ 144 AND 455
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

NOTICE OF DECLINE OF CONSENT TO BE HEARD BY A ‘MAGISTRATE JUDGE’ AND DEMAND FOR AN ARTICLE III JUDGE
$0.00 Add to cart -

Notary Protest Template, Breakdown, and Details (Template 1)
$500.00Original price was: $500.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

AFFIDAVIT: RIGHT TO TRAVEL and CANCELATION, TERMINATION, and REVOCATION of “For Hire” COMMERCIAL LICENSE
$999.00Original price was: $999.00.$99.99Current price is: $99.99. Select options -

VERIFIED NOTICE OF PERFECTED SECURED INTEREST AND CLAIM OF INTEREST IN ALL COURT BONDS, MONETARY INSTRUMENTS, CREDITS, SECURITY INTERESTS, INTANGIBLES, CHATEL PAPER, TRUST ASSETS, CRIS ACCOUNTS, SECURITIES, AND INSTRUMENTS, AND DEMAND FOR ACCOUNTING, RELEASE, AND DISBURSEMENT
$999.99Original price was: $999.99.$300.00Current price is: $300.00. Add to cart
DOCUMENTS
-

Trusts Breakdown and Types (Black’s Law): Everything is a TRUST
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Great Overlay: The BAR-Run Conversion of Americans into Wards — The Codification Process From Organic Sovereignty to Corporate Statutory Rule
$0.00 Add to cart -

NO Law Requires You to Registered your private automobile or property
$0.00 Add to cart -

UNITED STATES TREASURY INSTRUMENTS AND THE IRS TRUST SYSTEM: The Commercial Law Reality of Forms 56, 2848, 843, 1040, 1040-V, 1040-ES, 1040-NR, 1040-X, 1041, 1041-V, and 1042
$0.00 Add to cart -

GENERAL MEMORANDUM OF LAW Re: Misuse of the Term “Sovereign Citizen” as a Sanctionable, Prejudicial, and Defamatory Violation of Judicial Standards, Due Process, and Ethical Conduct
$333.00Original price was: $333.00.$24.99Current price is: $24.99. Add to cart -

BIRTH CERTIFICATE BOND COVER LETTER
$0.00 Add to cart -

national/non-citizen national STATUS CORRECTION, CLAIM of ENTIRE ESTATE, ALL ASSETS, AND RIGHTS
$150,000.00Original price was: $150,000.00.$13,000.00Current price is: $13,000.00. Buy product -

Library of Congress Certified: House Joint Resolution 192 of June 5 1933, Public Law 73-10
$0.00 Add to cart -

Affidavit or Truth: Sovereignty, Jurisdiction, Claim of Estate, Use of FRNs
$1,000.00Original price was: $1,000.00.$33.00Current price is: $33.00. Add to cart
BOOKS
-

™SOVEREIGN BLUEPRINT© An educational guide of Truth for reclaiming your assets, rights, and birth estate
$3,000.00Original price was: $3,000.00.$43.33Current price is: $43.33. Add to cart -

‘The Master Key’ by Charles F. Hannel, 1919
$0.00 Add to cart -

Bible Myths And Their Parallels In Other Religions – Year 1882
$0.00 Add to cart -

Ethiopian Bible – Year 1300
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Great Conversion and The “Legal” Architecture of Enslavement: How America Was Converted from a Republic of Sovereign People into a Corporate-Financial Trust System and How Sovereignty Was Replaced with Statutory Slaver
$79.99 Add to cart -

Magnetic Current – Ed Leedskalnin (1945)
$0.00 Add to cart
DICTIONARIES AND ENCYCLOPEDIAS
-

Black’s Law Dictionary 4th Edition – 1968
$240.00Original price was: $240.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

Black’s Law Dictionary 8th Edition – 2004
$36.00Original price was: $36.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

BOUVIERS’S LAW DICTIONARY AND CONCISE ENCYCLOPEDIA – VOLUME 3
$0.00 Add to cart -

Black’s Law Dictionary 7th Edition – year 2000
$18.00Original price was: $18.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart -

Black’s Law Dictionary 1st Edition – 1891
$0.00 Add to cart -

Black’s Law Dictionary 2nd Edition – 1910
$0.00 Add to cart -

OXFORD DICTIONARY OF LAW
$0.00 Add to cart -

The Concise Dictionary of Current English Adapted by H. W. FOWLER and F. G. FOWLER – 1919
$0.00 Add to cart -

Black’s Law Dictionary 3rd Edition – 1910
$197.00Original price was: $197.00.$0.00Current price is: $0.00. Add to cart
MOST VIEWED
Who is Responsible for the “Obligations” and/or BILLS, DRAFTS, CHECKS, FRNs,/Dollars?
Many people are banking incorrectly, misunderstanding the true nature of financial obligations and the protections available to them under the law. According to 18 U.S. Code § 8, an "obligation or other security...
Read MoreDischarging Debt Under UCC 3-603 and 3-311: Your Rights Explained
A bill of exchange can function as "legal tender" or "tender of payment," but its status depends on acceptance and context but regardless, if tendered correctly, it does discharge the debt and respective...
Read More“state citizen”/national vs “U.S. citizen”: Understanding the Distinctions and Implications
This explanation clarifies the distinction between state citizens and nationals in the context of U.S. law, emphasizing that individuals born in a state are primarily state citizens with allegiance to their state, not...
Read MoreFor Smart visionaries
Embrace the Wisdom of Time and Money
In the pursuit of your dreams, remember that money is but a means to an end, a tool in your hands to craft the life you envision. Invest it wisely, not just in financial endeavors, but in experiences that enrich your soul. Time, the most precious currency, is the foundation of your journey. Allocate it with care, for it is the true measure of wealth. Seize each moment, for in its passage lies the essence of a life well-lived. Let your pursuits be guided by purpose, and may every resource at your disposal serve to enhance the tapestry of your existence.

Live on Cardano. Designed for the jurisdiction of self. Suijuris Coin is a digital asset created to reflect one simple truth: You are the authority. No middleman. No permission. No plea. Built years ago and now holding a live USD value, Suijuris is a Cardano-native token quietly designed to support those building private remedy, lawful structures, and generational sovereignty. This isn’t a meme coin or hype drop. It’s a declaration of value—anchored in intention.

A limited fixed supply of just 3,300,000 coins with all coins being made available to the community.
$SUIJURIS: 94c754e211977cf2bf4e98d201d638679c963875fc8ffa330a0ad02b
• Blockchain: Cardano (ADA-native)
• Purchase: Immediate delivery to your wallet (Cardano wallet required)
• Minimum: 1 Suijuris Coin
• Bonus: Orders over X coins may unlock early access to private events or tools (optional upsell)

By holding Suijuris Coin, you:
• Support its activation toward full exchange listing
• Claim early access to private offerings, future tools, and workshops
• Align your energy with a currency that reflects your principles
Whether you're here to exit dependency, build with integrity, or simply say I see what's coming,
Suijuris Coin is for those who move with precision—not permission.

• Lawful self-governance (“suijuris” = of one’s own right • Value created outside of commercial dependency • Entry into a growing network of trust-based, sovereignty-aligned tools
See below or reach out to support!
Under IOHK’s leadership, Cardano was developed as a third-generation blockchain platform, with a strong emphasis on scientific research, peer-reviewed development, and sustainability.
1. Decentralization:
– Cardano, known for its commitment to decentralization, employs a unique consensus mechanism called Ouroboros. This ensures that the network remains secure and decentralized, allowing for a more robust and censorship-resistant platform compared to many other cryptocurrencies.
2. Blockchain Technology:
– Cardano’s blockchain is built on a scientifically-driven approach, utilizing extensive research and peer-reviewed academic studies. This approach sets it apart, offering a highly secure and scalable infrastructure designed to accommodate a wide range of applications.
3. Limited Supply:
– Like Bitcoin, Cardano has a finite supply, which is capped at 45 billion ADA. This controlled scarcity, combined with a meticulous approach to monetary policy, positions Cardano as an asset with a strong potential for long-term value appreciation.
4. Mining:
– Cardano uses a unique Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, making it energy-efficient and more environmentally sustainable compared to the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) system employed by Bitcoin. PoS also allows for greater participation from the community in the validation process.
5. Peer-to-Peer Transactions:
– Cardano’s focus on interoperability ensures seamless communication with other blockchains, potentially revolutionizing cross-chain transactions. This makes Cardano a versatile platform for a wide range of financial applications and smart contracts.
6. Pseudonymity:
– Cardano aims to enhance privacy by allowing users to choose whether or not to disclose their transaction details. This feature provides an additional layer of privacy compared to Bitcoin, offering users more control over their personal information.
7. Security:
– Cardano’s approach to security is rooted in its dedication to formal verification, a mathematical method for ensuring the correctness of code. This meticulous approach minimizes the risk of bugs or vulnerabilities, making Cardano one of the most secure platforms in the cryptocurrency space.
8. Store of Value:
– With its robust infrastructure and commitment to scientific principles, Cardano is emerging as a promising store of value in the digital asset landscape. Its focus on sustainability and long-term viability positions ADA as a reliable asset for preserving wealth.
9. Volatility:
– While Cardano, like all cryptocurrencies, experiences market fluctuations, its sustainable growth model and focus on long-term development contribute to a potentially more stable and resilient price trajectory compared to more speculative assets.
10. Global Reach:
– Cardano’s commitment to inclusivity and accessibility ensures that it remains a global platform accessible to anyone with an internet connection, providing opportunities for financial inclusion on a worldwide scale.
Cardano’s meticulous scientific approach, commitment to sustainability, and emphasis on long-term value make it a unique and promising player in the world of cryptocurrencies.
$SUIJURIS is the native cryptocurrency for Realworldfare ecosystem, and built natively for the Cardano blockchain.
Max Supply = 3.3 Million
100% of supply to community.
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It was introduced in a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” in 2008, and the Bitcoin network officially came into existence with the release of its open-source software in January 2009.
Here are some key characteristics and features of Bitcoin:
1. Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes) spread across the globe. This means it’s not controlled by any single entity, such as a government or a central bank.
2. Blockchain Technology: Transactions on the Bitcoin network are recorded in a public ledger called the blockchain. The blockchain is a series of blocks, each containing a set of transactions. This ledger is maintained and verified by the network of nodes.
3. Limited Supply: There is a maximum supply cap of 21 million Bitcoins. This scarcity is programmed into the Bitcoin protocol and contributes to its perceived value.
4. Mining: The process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain is called mining. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. When a puzzle is solved, a new block is added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with newly created Bitcoins, along with transaction fees.
5. Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Bitcoin enables direct transactions between parties without the need for intermediaries like banks. This allows for fast and relatively low-cost international transactions.
6. Pseudonymity: While Bitcoin transactions are recorded on the blockchain, the identities of the participants are hidden behind cryptographic addresses. This provides a level of privacy, although it’s not completely anonymous.
7. Security: Bitcoin transactions are highly secure due to the cryptographic nature of the network. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes very difficult to alter.
8. Store of Value: Many people consider Bitcoin as a form of digital gold, viewing it as a store of value and a hedge against inflation.
9. Volatility: Bitcoin’s price is known for its high volatility. It can experience significant price fluctuations over short periods of time.
10. Global Reach: Bitcoin is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, making it a truly global currency.
Bitcoin has had a significant impact on the world of finance and has paved the way for the development of thousands of other cryptocurrencies. It’s used for a variety of purposes, including online purchases, investment, remittances, and as a means of transferring value across borders.
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures security, transparency, and immutability.
Here’s how it works:
1. Decentralization: Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single entity (like a bank or government) has control over the data, blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes). Each node has a copy of the entire ledger.
2. Blocks: Transactions are grouped together into blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions and a unique identifier called a cryptographic hash.
3. Chaining: These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, creating a chain. This linkage is achieved through cryptographic hashes. Each block’s hash contains information about the previous block’s hash.
4. Consensus Mechanisms: To validate transactions and add a new block to the chain, participants in the network must reach a consensus. This process varies based on the blockchain’s specific protocol (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, etc.).
5. Immutability: Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes extremely difficult to alter or remove the information. This is due to the cryptographic nature of the hash functions and the fact that the information is distributed across many nodes.
6. Transparency: The ledger is public and transparent, meaning that anyone can view the entire transaction history. However, personal identities are hidden behind cryptographic addresses.
7. Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of the blockchain makes it highly secure against hacking or fraud. Any attempt to alter a block would require immense computational power and would need to be validated by the majority of the network.
Blockchain technology has found applications in various industries beyond cryptocurrencies. It’s used for things like smart contracts, supply chain management, voting systems, healthcare, and more. Its ability to provide a secure and transparent ledger for transactions has revolutionized how we think about data management and has the potential to disrupt many traditional industries.
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional paper currencies issued and regulated by governments (known as “fiat” currencies ), cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology.
Here are some key characteristics of cryptocurrencies:
1. Digital Nature: Cryptocurrencies exist only in digital form and have no physical counterpart like coins or banknotes. They are stored electronically in digital wallets.
2. Decentralization: Most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks of computers (nodes) spread across the globe. This means there’s no central authority, like a government or bank, controlling or regulating the currency.
3. Blockchain Technology: Transactions made with cryptocurrencies are recorded in a public ledger called a blockchain. The blockchain is a series of blocks, each containing a set of transactions. This ledger is maintained and verified by the network of nodes.
4. Security: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. This makes it very difficult for unauthorized parties to alter transaction data.
5. Anonymity and Pseudonymity: While transactions on a blockchain are recorded, the identities of the participants are often hidden behind cryptographic addresses. This provides a level of privacy, although it’s not completely anonymous.
6. Limited Supply: Many cryptocurrencies have a maximum supply cap, meaning there’s a finite amount that can ever be created. This controlled scarcity can contribute to the value of the cryptocurrency.
7. Transparency: The transaction history of each cryptocurrency is recorded on a public ledger, allowing anyone to view the details of transactions. However, personal information is not publicly linked to the transactions.
8. Global Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies can be accessed and used by anyone with an internet connection, making them truly global currencies.
9. Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can be highly volatile, with significant fluctuations over short periods of time. This can present both opportunities and risks for investors.
10. Use Cases: Cryptocurrencies can be used for various purposes, including online purchases, investment, remittances, smart contracts, decentralized applications (DApps), and as a means of transferring value across borders.
A cryptocurrency wallet is a software program or a physical device that allows users to securely store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies. It manages a user’s private and public keys, which are essential for interacting with blockchain networks. Here’s how a cryptocurrency wallet works:
1. Private and Public Keys:
– Each cryptocurrency wallet contains a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key and a public key.
– The private key is a secret code known only to the wallet owner. It’s used to sign transactions and access the wallet’s funds.
– The public key is a public identifier that is shareable and used to receive funds. It’s derived from the private key.
2. Address:
– The public key, or a hashed version of it, is used to generate a wallet address. This address is like an account number for the cryptocurrency network and is used to receive funds.
3. Transactions:
– When a user wants to send cryptocurrency, they create a transaction using their wallet.
– The transaction includes the recipient’s address, the amount of cryptocurrency to be sent, and a digital signature created with the private key to verify the transaction’s authenticity.
4. Signing Transactions:
– The wallet uses the private key to digitally sign the transaction. This signature proves that the transaction was authorized by the rightful owner of the funds.
5. Broadcasting Transactions:
– Once the transaction is signed, it’s broadcast to the cryptocurrency network.
– The network verifies the transaction’s validity by checking the digital signature and other criteria.
6. Blockchain Confirmation:
– The transaction is included in a block, which is then added to the blockchain. This process is known as confirmation.
– The number of confirmations a transaction requires depends on the cryptocurrency and the associated security protocol.
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallets:
1. Software Wallets (Hot Wallets):
– These are applications or software programs installed on computers, smartphones, or tablets.
– Examples include desktop wallets (installed on PCs), mobile wallets (for smartphones), and web wallets (accessed through a web browser).
2. Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets):
– These are physical devices designed solely for storing cryptocurrency keys offline.
– They provide an extra layer of security by keeping the keys away from internet-connected devices.
3. Paper Wallets:
– A paper wallet involves printing the public and private keys onto a piece of paper. This method is highly secure because it’s not connected to the internet.
4. Multi-Signature Wallets:
– These require multiple private keys to authorize a transaction, providing additional security.
It’s crucial to keep the private key secure, as anyone with access to it has control over the associated funds. Losing access to the private key can result in the permanent loss of the stored cryptocurrencies. Therefore, it’s recommended to back up private keys and store them in a secure location.